

They are seen in patients with altered levels of consciousness. It is hypothesized that they occur due to structural or metabolic abnormalities at the thalamocortical levels due to the changes in the thalamocortical relays. Triphasic waves are seen diffusely with bifrontal predominance and are synchronous. The first phase is always negative, hence the name triphasic waves. They are sharply contoured with three phases.

They are high amplitude sharp waves, with the duration of each phase longer than the next.
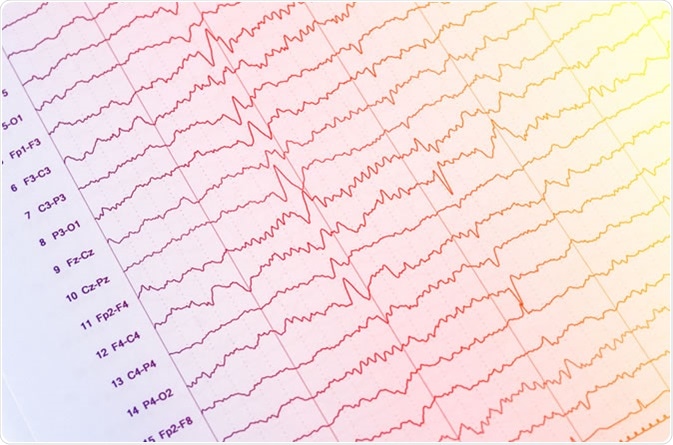
However, these are nonspecific and can be seen in any metabolic encephalopathy. Triphasic waves were first believed to be pathognomic of hepatic encephalopathy. Triphasic waves: Triphasic waves were initially described in 1950 by Foley, and in 1955 Bickford and Butt gave it the name. Medications like sedatives (phenobarbital, benzodiazepines) commonly cause diffuse beta activity.

Focal beta activity sometimes seen in structural lesions and also in various epilepsies (generalized fast activity/GFA). Beta activity is present in the frontal regions of the brain and can spread posteriorly in early sleep. Delta waves can be seen in drowsiness and also in very young children however, the appearance of focal delta activity can be abnormal (see below). However, in certain comatose states, there can be diffuse alpha activity (alpha comma) and may be considered pathognomonic. For example, alpha waves are seen over the posterior head regions in a normal awake person and considered as the posterior background rhythm. The electroencephalographer is expected to have the significant skills to recognize artifacts, and also an understanding of normal, benign variants. This article reviews the abnormal waveforms in EEG recordings.Įven normal EEG waveforms can be considered potentially abnormal, depending upon various factors. Deep electrical activity of the brain is not well sampled in an EEG using extracranial electrode monitoring.Ībnormal waveforms seen in an EEG recording include epileptiform and non-epileptiform abnormalities. In order to identify abnormal waveforms in EEG, the reader should have a basic understanding of the normal EEG pattern in various physiological states in children and adults. It represents fluctuating dendritic potentials from superficial cortical layers, which are recorded in an organized array pattern and require voltage amplification to be captured. It is a tracing of voltage fluctuations versus time recorded from multiple electrodes placed over the scalp in a specific pattern to sample different cortical regions. Electroencephalography (EEG) was first used in humans by Hans Berger in 1924.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
